Working Hours
- Monday - Friday
09:00 - 19:00
Contact
Ask the Experts
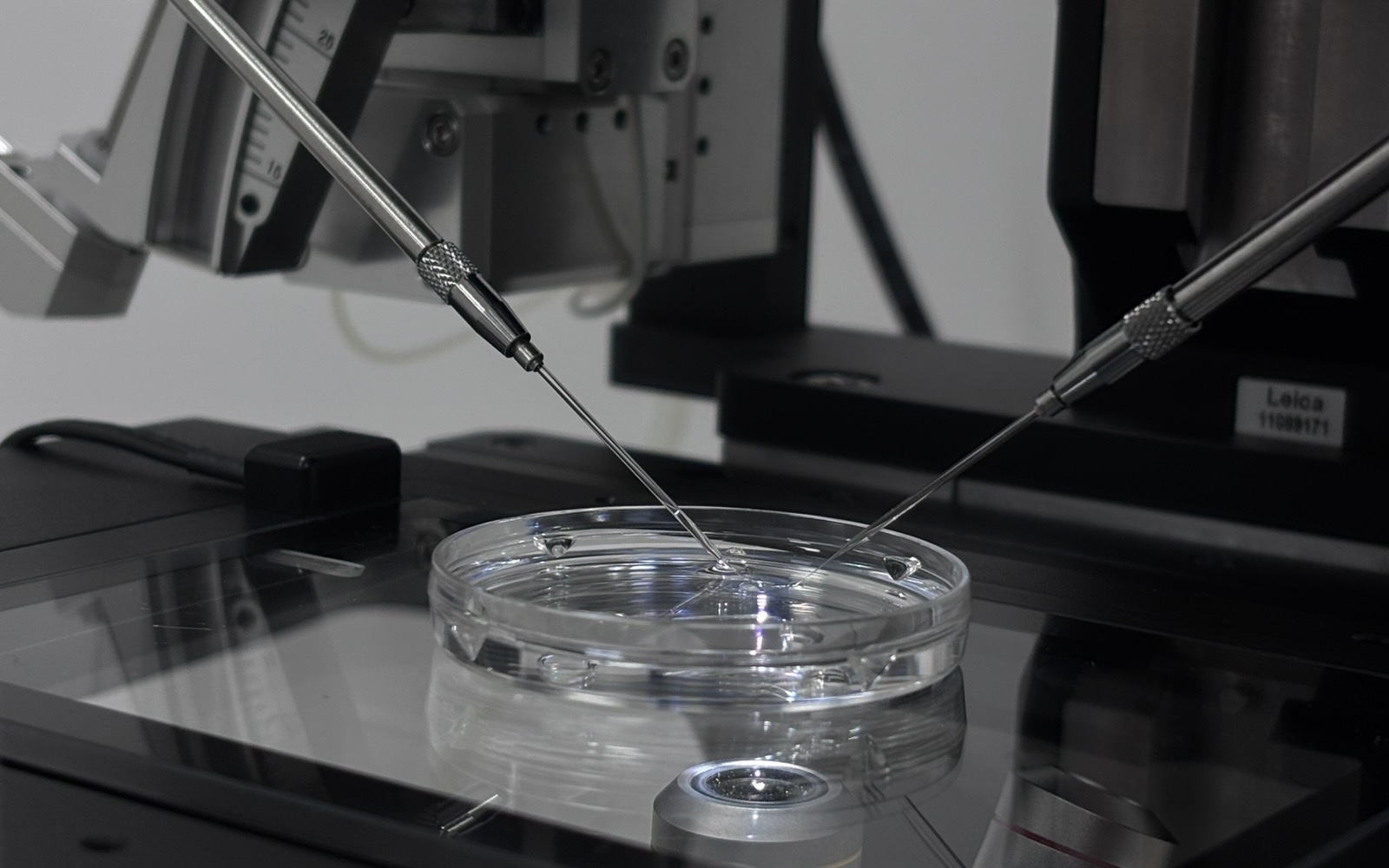
In vitro fertilization from the natural cycle
In vitro fertilization (IVF) can be done in a spontaneous cycle without stimulation drugs. The world's first child after IVF was born from the procedure in a spontaneous cycle.
How is IVF done from a natural cycle?
Physiologically, one egg cell is released every month in women who have regular cycles. In this process, natural selection selects one egg cell that will ovulate. The egg is 0.1 mm and cannot be seen on ultrasound.
Indirect egg maturation is monitored through the follicle growth measured by ultrasound.
During the procedure, 2-3 ultrasound examinations are performed.
When the follicle reaches a certain size, luteinizing hormone (LH) and estradiol from the blood are analyzed to determine the time when ovulation will occur. Egg aspiration is done on the expected day of ovulation.
On the same day, the partner gives a semen sample and fertilization is done in the laboratory. A "stop injection" of beta chorionic gonadotropin (beta hCG) may be given at the end for maturing the egg. In this case, aspiration is done 34-36 hours after administration of beta hCG and the process is called a modified spontaneous cycle. Aspiration is most often done without or under local anesthesia.
Embryo transfer is done on the second, third or fifth day after aspiration.
Who are the candidates for the IVF in the spontaneous cycle?
- Couples where the woman is younger than 38 years old with regular cycles, a short period of infertility and abnormal semen analysis;
- Couples where the woman has a reduced ovarian reserve and where a larger number of eggs cannot be obtained with conventional therapy;
- Couples who do not want conventional drug stimulation for economic, medical or other reasons.
When is IVF from a natural cycle not advised?
IVF in a spontaneous cycle is not advised in:
- couples where the woman is over 40 years old and has a good ovarian reserve;
- in couples where the woman does not have regular cycles;
- in couples who have had multiple unsuccessful IVF procedures where the woman has good ovarian reserve.
What should patients know about natural cycle IVF?
It is very important that couples understand the whole process, because the more they understand, the easier it will be for them to go through the IVF procedure.
There is a risk of not getting an egg.
The time to achieve pregnancy is longer after the procedure in a spontaneous cycle than after the IVF procedure where ovarian stimulation was used.
The success of the procedure increases with the number of eggs obtained.
In women with significantly reduced ovarian reserve, IVF with conventional stimulation has the same effect as IVF in a spontaneous or modified spontaneous cycle.
Frequently asked questions: expert advice

Answered by Dr. Milan Milenković
How many eggs are retrieved by aspiration in a spontaneous cycle?
One egg is retrieved by aspiration in a spontaneous cycle. In about 30-35% of cases, no egg is retrieved during aspiration.
What fertilization method is used in the laboratory?
For egg fertilization in the IVF process from a spontaneous cycle, both the conventional IVF method and the ICSI method are used, depending on the semen analysis, as well as the technique used by the laboratory. The percentage of fertilization is about 50-60%.
Is progesterone used after embryo transfer in this process?
Progesterone therapy is not required after IVF and after the transfer in a spontaneous cycle, although it is often used in practice.
What is the success of the IVF from the natural cycle?
The success of IVF in a spontaneous cycle depends on the age of the woman and the duration of infertility.
In about 50% of couples who performed IVF in a spontaneous cycle, embryo transfer is performed.
8-14% of couples have a child after embryo transfer.
The cumulative chance of having a child after 6 embryo transfers in women under 35 years old is 70%, and in women aged 41-42 years it is 25-30%. 10% of women over the age of 42 give birth to a child after 6 embryo transfers.
Is there a risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)?
There is no risk of OHSS in the natural cycle IVF process.